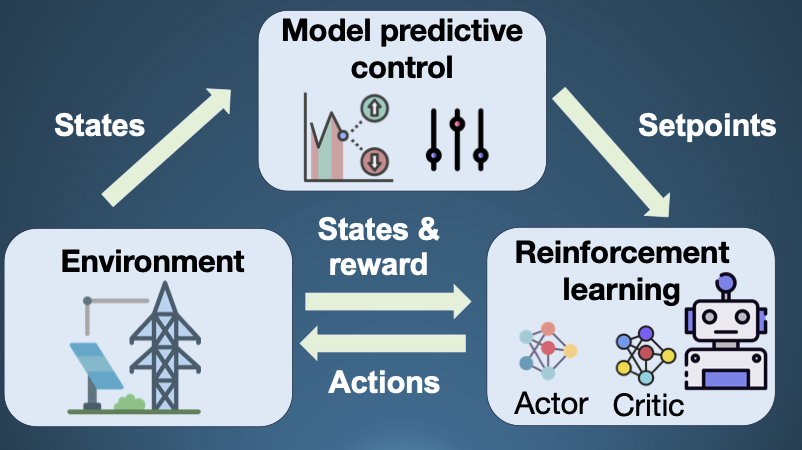
Predictive Control & Optimisation with Machine Learning
Nonlinear/economic MPC with state and parameter estimation, Gaussian-process surrogates and reinforcement learning for safe, sample-efficient, performance-driven operation under uncertainty.
We work in dynamic process modelling, model-based control, and machine learning, developing methods that link data and physics to improve real-world systems. Our research spans mineral processing and emerging decarbonisation technologies, focusing on how hybrid models and digital twins can enable real-time prediction, optimisation, and control. These tools are key to advancing the efficiency and sustainability of industrial processes that drive the global energy transition.
New PhD studentship (Stipend + UK Fees) — apply by December 31, 2025: View details on FindAPhD →

Nonlinear/economic MPC with state and parameter estimation, Gaussian-process surrogates and reinforcement learning for safe, sample-efficient, performance-driven operation under uncertainty.
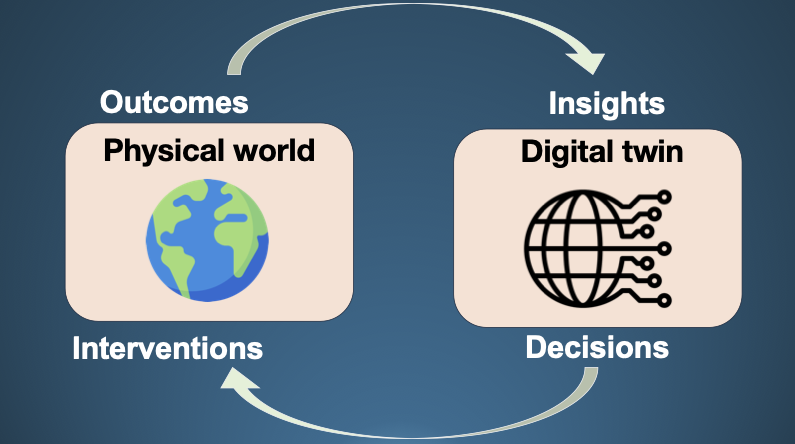
Physics-informed and machine-learning models combined into reliable virtual replicas for real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and control of complex processes.
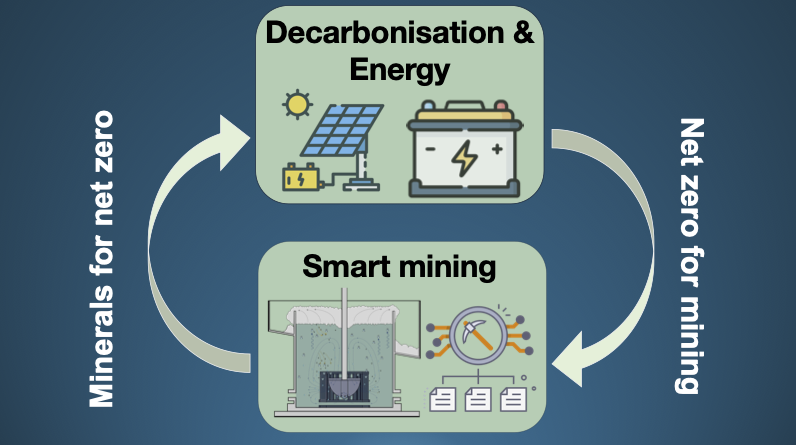
Digita tools application across froth flotation, heap leaching, and SAG mills, and in clean-energy systems including blue hydrogen, battery control (RL-MPC), and AI-assisted lifecycle analysis.
I am an Assistant Professor (UK Lecturer) in Process Systems Engineering in the Department of Chemical Engineering at UCL. I am also an Early Career Advisory Board member of Control Engineering Practice, a journal of the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC).
I hold a PhD in Earth Science and Engineering from Imperial College London and obtained MEng and MSc degrees in Chemical Engineering from Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María in Valparaíso, Chile. I previously worked as a Postdoctoral Researcher at the Sargent Centre for Process Systems Engineering, Imperial College London, and was appointed Assistant Professor at Brunel University London in 2024.







Published in Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2025
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Navia, D., Neethling, S. J., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2025). Centralised economic model predictive control of froth flotation banks with experimental implementation. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 224, 467-481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2025.11.037
Published in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025
Recommended citation: Davies, W. G., Quintanilla, P., Yang, Y., & Masoudi Soltani, S. (2025). Global sensitivity analysis of blue hydrogen production: A comparative study using machine learning. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 190, 152153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2025.152153
Published in Control Engineering Practice, 2025
Recommended citation: Mancilla, C., Bruna, R., Quintanilla, P., & Navia, D. (2025). Dynamic real-time optimization to mitigate critical state effects in expert-controlled SAG mills. Control Engineering Practice, 165, 106589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2025.106589
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2025
Recommended citation: Olivares, B., Araya, B., Quintanilla, P., & Navia, D. (2025). Saturation regulation in heap leaching: A nonlinear model predictive control approach. Minerals Engineering, 229, 109346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2025.109346
Published in Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2025
Recommended citation: Wang, Y., del Río Chanona, E. A., & Quintanilla, P. (2025). Gaussian Process Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Online Partially Observable Systems: An Application to Froth Flotation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5c00660
Published in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Elhalwagy, A., Duan, L., Masoudi Soltani, S., Lai, C. S., Foroudi, P., Huda, M. N., & Nandy, M. (2025). Artificial intelligence and robotics in the hydrogen lifecycle: A systematic review. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 113, 801-817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2025.03.016
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2025
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Fernández, F., Mancilla, C., Rojas, M., & Navia, D. (2025). Digital twin with automatic disturbance detection for an expert-controlled SAG mill. Minerals Engineering, 220, 109076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2024.109076
Published in Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 2024
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Navia, D., Neethling, S., & Brito-Parada, P. (2024). Experimental Implementation of an Economic Model Predictive Control for Froth Flotation. Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 53, 1759-1764. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-28824-1.50294-5
Published in IEEE, 2024
Recommended citation: González, R. A., & Quintanilla, P. (2024). Grey-box Recursive Parameter Identification of a Nonlinear Dynamic Model for Mineral Flotation. IEEE, 10th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), pp. 2967-2972, doi: 10.1109/CoDIT62066.2024.10708161
Published in IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Navia, D., Neethling, S. J., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2023). Evaluation of Changes in Feed Particle Size within an Economic Model Predictive Control Strategy for Froth Flotation. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 56(2), 2317-2322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.1200
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2023
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Navia, D., Neethling, S. J., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2023). Economic model predictive control for a rougher froth flotation cell using physics-based models. Minerals Engineering, 196, 108050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2023.108050
Published in MethodsX, 2023
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Navia, D., Moreno, F., Neethling, S. J., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2023). A methodology to implement a closed-loop feedback-feedforward level control in a laboratory-scale flotation bank using peristaltic pumps. MethodsX, 10, 102081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2023.102081
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2022
Recommended citation: Mesa, D., Quintanilla, P., & Reyes, F. (2022). Bubble Analyser — An open-source software for bubble size measurement using image analysis. Minerals Engineering, 180, 107497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107497
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2021
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Neethling, S. J., Mesa, D., Navia, D., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2021). A dynamic flotation model for predictive control incorporating froth physics. Part II: Model calibration and validation. Minerals Engineering, 173, 107190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107190
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2021
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Neethling, S. J., Navia, D., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2021). A dynamic flotation model for predictive control incorporating froth physics. Part I: Model development. Minerals Engineering, 173, 107192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107192
Published in Materials Proceeding, 2021
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P.; Neethling, S.J.; Brito-Parada, P.R. Development and Validation of a Dynamic Model for Flotation Predictive Control Incorporating Froth Physics. Mater. Proc. 2021, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005013
Published in Minerals Engineering, 2021
Recommended citation: Quintanilla, P., Neethling, S. J., & Brito-Parada, P. R. (2021). Modelling for froth flotation control: A review. Minerals Engineering, 162, 106718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106718
Published in Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019
Recommended citation: Navia, D., Puen, A., Quintanilla, P., Briceño, L., & Bergh, L. (2019). On dealing with measured disturbances in the modifier adaptation method for real-time optimization. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 128, 141-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.06.004
Published in Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 2018
Recommended citation: Navia, D., Puen, A., Quintanilla, P., Bergh, L., Briceño, L., & de Prada, C. (2018). A Proposal to Include the Information of Disturbances in Modifier Adaptation Methodology for Real Time Optimization. Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 43, 1081-1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64235-6.50189-3

Bubble Analyser is a comprehensive open-source app that processes images of bubbles, enabling users to quantify bubble size distribution. The tool is free to use and modify under the GNU General Public License, making it accessible to everyone.
Developed in collaboration with Imperial College London and IntelliSense.io, Bubble Analyser was designed with expandability and an easy-to-use interface in mind. It is also available as an executable version for easy deployment.
With Bubble Analyser, you can efficiently analyse bubble images and extract quantitative insights into complex processes. Visit BubbleAnalyser.com →